Bihar Board 12th Biology Model Papers
Bihar Board 12th Biology Model Question Paper 3 in English Medium
Time : 3 Hours 15 Min
Total Marks : 70
Instructions for the candidates:
- Candidates are required to give answers in their own words as far as practicable.
- Figures in the right-hand margin indicate full marks.
- While answering the questions, the candidate should adhere to the word limit as for as practicable.
- 15 Minutes of extra time has been allotted for the candidates to read the questions carefully.
- This question paper is divided into two sections: Section – A and Section – B
- In Section – A, there are 35 objective type questions which are compulsory, each carrying 1 mark. Darken the circle with blue/black ball pen against the correct option on OMR Sheet provided to you. Do not use Whitener/Liquid/ Blade/Nail on OMR Sheet otherwise result will be treated as invalid.
- In Section – B, there are Non-objective type questions. There are 18 Short answer type questions, out of which any 10 questions are to be answered. Each question carries 2 marks. Apart from this, there are 6 long answer type questions, out of which any 3 of them are to be answered. Each question carries 5 marks
- Use of any electronic device is prohibited.
Objective Type Questions
There are 1 to 35 objective type questions with 4 options. Choose the correct option which is to be answered on OMR Sheet. (35 x 1 = 35)
Question 1.
Fusion of male gametes with secondary nuclei is called
(a) Syngamy
(b) Triple fusion
(c) Geitenogamy
(d) Cleistogamy
Answer:
(b) Triple fusion
![]()
Question 2.
A large cluster of ribosome is called
(a) Megasome
(b) Microsome
(c) Polyribosome
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Polyribosome
Question 3.
Which of the following is a biofertilizer?
(a) Cynobacteria
(b) Mycorhiza
(c) Symbiotic bacteria
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 4.
Middle piece of a mammalian sperm contains
(a) Nucleus
(b) Centriole
(c) Mitochondria
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Mitochondria
Question 5.
Acrosome is present in
(a) Sperm
(b) Ova
(c) Ovary
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Sperm
Question 6.
Anemophily can be best seen in
(a) Sunflower
(b) Maize
(c) Pig
(d) Yucca
Answer:
(b) Maize
Question 7.
Citric acid is produced by
(a) Acetobacter Aceti
(b) Yeast
(c) Aspergillus niger
(d) Streptococcus
Answer:
(c) Aspergillus niger
![]()
Question 8.
Which of the following cells present in mammalian testes help to nourish sperms?
(a) Leydig cell
(b) Male germ cells
(c) Autosomes
(d) Sertoli cells
Answer:
(d) Sertoli cells
Question 9.
Which one of the following is false fruit?
(a) Mango
(b) Banana
(c) Apple
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Apple
Question 10.
Binary fission occurs in
(a) Lotus
(b) Amoeba
(c) Water hyacinth
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(b) Amoeba
Question 11.
The concept of Lac operon was given by
(a) Beadle & Tatum
(b) Watson and Crick
(c) Jacobe and Monad
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Jacobe and Monad
Question 12.
The term ecosystem was coined by
(a) Lamarck
(b) Darwin
(c) A.G. Tansley
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) A.G. Tansley
Question 13.
Minamata disease is due to pollutant
(a) H2
(b) SO2
(c) Mercury
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(b) SO2
Question 14.
Which one of the following is the high-milk yielding variety of cow?
(a) Holstein
(b) Pashmina
(c) Dorset
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Holstein
![]()
Question 15.
In plant meiosis occurs in
(a) Pollen grain
(b) Anther
(c) Root tip
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Anther
Question 16.
Example of corm is
(a) Onion
(b) Ginger
(c) Colocasia
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Colocasia
Question 17.
Which of the following is chain initiation of codon?
(a) AUG
(b) UAG
(c) UUA
(d) CCC
Answer:
(a) AUG
Question 18.
Widal Test is done to confirm
(a) Typhoid
(b) Malaria
(c) Filaria
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Typhoid
Question 19.
Which microbe is used in manufacturing of bread?
(a) Anabena
(b) Algae
(c) Baker’s Yeast
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Baker’s Yeast
Question 20.
Human genome project was discovered by
(a) Watson and Crick
(b) Beadle and Tatum
(c) Francis Collins and Roderick
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Francis Collins and Roderick
Question 21.
Embryo sac is created by which of the following?
(a) Megaspore
(b) Microspore
(c) Both
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Megaspore
![]()
Question 22.
Down’s Syndrome in child is due to
(a) Gene mutation
(b) Monosomy
(c) Trisomy
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Trisomy
Question 23.
On which insect group Bt-toxin is effective?
(a) Dipteron
(b) Lepidopteron
(c) Choleopteron
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 24.
Miller prepared in laboratory
(a) Amino acid
(b) Ammonia
(c) Hydrogen
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Amino acid
Question 25.
Dinosaurs found in the era of
(a) Permian
(b) Modem
(c) Carboniferrous
(d) Jurassic
Answer:
(d) Jurassic
Question 26.
PCR is used in Amplification of
(a) Protein
(b) Enzyme
(c) Segment of DNA
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Segment of DNA
Question 27.
Genetically engineered human insulin is made by
(a) Plant
(b) Yeast
(c) Bacterium
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Bacterium
Question 28.
What is Mala D?
(a) Contraceptive
(b) Vitamins
(c) Medicine for fever
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Contraceptive
![]()
Question 29.
Which among is cancer?
(a) Leukemia
(b) Lymphoma
(c) Liposa
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 30.
Second trophic level in lake is
(a) Phytoplankton
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Both
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Zooplankton
Question 31.
Which of the following is known as green house gas?
(a) Methane
(b) CFC
(c) C02
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 32.
The first human like being the homonid was called
(a) Homo sapiens
(b) Homo erectus
(c) Homo habilis
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Homo habilis
Question 33.
AIDS is STD which is transmitted through
(a) Sexual contact
(b) Blood transmission
(c) Contaminated syringe
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
![]()
Question 34.
The virus which cause cancer is known as
(a) TMV
(b) Oncogenic virus
(c) Bacteriophage
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(b) Oncogenic virus
Question 35.
Ozone layer is found in
(a) Troposhpere
(b) Mesosphere
(c) Stratosphere
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) Stratosphere
Non-Objective Type Questions
Short Answer Type Questions
In this section, there are 18 short answer type question (each carryies 2 marks) out of which answers any ten (10) questions. (10 x 2 = 20)
Question 1.
Explain contact inhibition?
Answer:
Uncontrolled cell division and proliferation growth & multiplication is sign of cancer cells & cancer disease. Cancerous cells are called malignant neoplasm, which develops on neighboring cells (by taking nutritive elements from them) grow and multiply. At last these cancerous cells kills the neighboring cells. These cancerous cells when come in contact with normal cell, they inhibit the growth and dynamic of these cells. This property of cancer cells are called contact inhibition.
Question 2.
Write the effects of Acid Rain.
Answer:
Effects of Acid Rain:
- Acid rain damages a number of heritage monuments due to deposition of acids, eg. Statue of Liberty, Taj Mahal etc.
- Acid rain kills the useful soil microbial community thus disturbing terrestrial ecosystems.
- In the aquatic ecosystem acid rain below 4 pH causes death of planktons, molluscs and fishes, therefore it disturbs the food chain.
Question 3.
How does killer T-cells act?
Answer:
T-cells attack directly and destroy antigens. In the process, these cells move to the site of invasion and produce chemicals that attract phagocytes and stimulate them so that they can feed more vigorously on antigens. They also produce substances that attract other T-cells.
Question 4.
Describe the symptoms & preventions of malaria disease.
Answer:
Symptoms :
- Fever with coldness, chill, headache & muscular pain.
- Decrease in RBC count.
- Spleen increases in size
- Fever comes alternatively at 48 hours.
Preventions :
(a) Through Destroying Mosquitoes – Malaria is spread by the bite of female anophelese mosquitoes, therefore, destroying them, we can prevent the disease. For this spraying of DDT & Kerosine and their biological control through Gambusia fish is very useful.
(b) Prevention through infection – Every person should use mosquito net. If necessary mosquito cream available in market should be used for protection from mosquito bite. Medicines like Quinine and Paludrin may be used for treatment of malaria.
Question 5.
Write short notes on tRNA.
Answer:
Transfer RNA : A transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule has the form of a cloves leaf that results from self
folding and base pairing, creating paired stems and unpaired loops. It has four regions (a) Carrier end (b) Recognition end (c) Enzyme site (d) Ribosome site. It forms about 10¬15% of the total RNA.
Question 6.
Write any four bacterial diseases and its pathogens.
Answer:
Cholera – Vibrio cliolerae
Tuberculosis – Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Titanus – Clostridium tetani
Pneumonia – Streptococcus pneumoni
![]()
Question 7.
Name the enyzmes which are employed in genetic engineering.
Answer:
Following enzymes are employed in genetic engineering:
(a) Lysing enzymes – Lysozyme
(b) Cleaving enzymes
(i) Exonuclease
(ii) Endonuclease
(iii) Restriction endonuclease
(c) Synthesizing enzymes
(i) DNA polymerase
(ii) Reverse transcriptase
(d) Joining enzymes
(e) Alkaline phosphotase
Question 8.
Give differences between Nucleoside and Nucleotide.
Answer:
| Nucleoside | Nucleotide | |
| 1. | A nucleoside consists of a nitrogenous base covalently attached to sugar but without the phosphate group. | 1. A nucleotide consists of nitrogenous base, asugar and one to three phosphate group. |
| 2. | Nature is Alkaline. | 2. Nature is Acidic. |
| 3. | They are components of nucleotides | 3. They are components of energy carriers and co-enzymes. |
Question 9.
Mention the names of Five diseases caused by Helminthes. Give symptoms & control of one disease.
Answer:
Name of disease:
- Ascariasis Ascaris
- Filariasis
Causative agent:
- lumbricoides
- Wuchereria bancrafti
Syptoms of Ascariasis-1. Loss of Apetite 2. Pain in stomach 3. Increased number of worms in intestine may block the cavity which may create problem.
Control-
- After 12 hrs. of fasting one dose of Hexil resorsinol is given due to which worms come outside with stool.
- Tetrachloroethylene and oil of Chenopodium in mixture is very effective.
- Hetrazon & Piprazinhydrate drugs are helpful.
![]()
Question 10.
What is significance of Parthenogenesis?
Answer:
Significance of Parthenogenesis :
- It helps in determining the sex of an animal as in honey bee.
- It overcomes the wastage of energy spent upon the process of mating and fertilization by an animal.
- It rapidly increases the number of animals in a population.
Question 11.
What is ’In situ’ conservation? What is its benefit?
Answer:
In situ conservation is the process of protecting the endangered species of plant or animal in the natural habitat either by protecting or cleaning up the habitat itself or by defending the species from predators. It helps in recovering the population in the surroundings where they have developed their distinctive features.
Question 12.
Expand MTP. Why it is so done?
Answer:
MTP stands for Medical Termination of Pregnancy. It is the intentional termination of pregnancy before full term. It is done to get rid of unwanted pregnancy due to rapes, or unprotected intercourse or failure of the contraceptive used during coitus. It has a significance role in decreasing the population though it is not performed for that purpose.
Question 13.
Describe the functions of antibody.
Answer:
- Antibody neutralizes the toxins produced by bacteria.
- By combining with antigen, antibody makes a macromolecular insoluble complete substance which inactivates the vital function of antigen.
- By oponization antibody get the bacteria in such a way that phagocytes identify them easily.
Question 14.
Write on control of sound pollution.
Answer:
Control of Noise Pollution :
- There could be developed gadgets to control noise at source of noise.
- Industrial units should be established away from high density populated areas.
- Loudspeakers should be banned.
- Sound absorbers should be used.
- For control of sound pollution the laws should be enforced effectively.
Question 15.
Write short notes on Lamarckism.
Answer:
French naturalist Lamarck has said that ’evolution of life forms had been driven by use and disuse of organs. He gave the example of Giraffes who in an attempt to forage leaves on tall trees had to adapt by elongation of their necks. As they passed on the acquired character of elongated neck to succeeding generations. Giraffe slowly over the years, came to acquire long necks.
![]()
Question 16.
What do you mean by term-mycorrhiza?
Answer:
It is the symbiotic association of fungal hyphae roots of higher plants. The fungal hyphae absorbs phosphorus from the soil and passes it to the plant. The plant also gets other benefits such as resistance to root-borne pathogens, tolerane to salinity and drought and increase in growth and development. In turn, the fungal hyphae get the nutrition from the plants.
Question 17.
What is test cross? Give its utility.
Answer:
Test cross : It is a cross between Fj hybrid and the recessive parent. The hybrid of F( generation, that is produced by inter-crossing two different parents may be similar phenotypically but genotypically, it may be heterozygous. To confirm the purity of Ft hybrid whether it is homozygous or heterozygous a test cross is done.
- If the test cross yields offsprings of 50% dominant and 50% recessive character, then the F[ hybrid is heterozygous. It shows (1:1) test ratio for monohybrid cross and (1 : 1 : 1 : 1) for dihybrid cross.
- If the test cross yields all the dominant character, then the Fj hybrid is homozygous.
Question 18.
State the relationship between linkage and crossing over.
Answer:
The linked genes do not always remain linked but are occasionally departed from other members of their linkage groups by crossing over. But the frequency of crossing over depends upon the distances between the various genes located on the same chromosome.
If the distances between the genes is more, then chances of crossing over and recombination are more. If the genes are closely placed on the same chromosome and the frequency of their separation is less than 50%, then there are less chances of departure of crossing over. In this case, the genes will remain linked and the progeny will be parental type.
Long Answer Type Questions
There are 6 long answers type question (each carrying 05 marks) out of which answers any three questions. (5 x 3 = 15)
Question 19.
What do you understand by Polyembryony? Describe it in detail. Discuss the Mendel’s Law of Inheritance.
Answer:
Occurrence of more than one embryo in a seed is referred to as polyembryony. Polyebryony was discovered by Leeuwenhoek in 1719. It is mostly found in gymnosperms and less found in angiosperms (eg. Mango, lemon etc.). It is of two types-true polyembryony and false polyembryony.
Causes of polyembryony are as follows :
- When more than one embryo sac in ovule;
- When more than one egg cell in embryo sac;
- When after fertilization, egg is separated in many small parts and every part forms a embryo;
- When any cell of embryo sac forms embryo;
- When embryo is formed by outer cells of embryo sac.
Importance of polyembryony are:
(a) It is very important for horticulture scientists.
(b) By this same types of plants may be formed.
(c) Characters of mother plants are present in daughter plants.
There are four principles of Mendel’s law of inheritance which are based on Monohybrid and Polyhybrid crosses.
(a) Principles of paired factors: The determination of characters in an organism (diploid) is marked by atleast two factors. Such factors are present on two chromosomes of the same locus.
(b) Law of dominance: In any heterozygous organism the representation of characters takes place by two contrasting characters in which one is dominant while the other is recessive.
(c) Law of Segregation: Two factors of any character who remain together can not mix with one another. However they get separated during gametogenesis.
(d) Law of Independent Assortment: According to this principle, two factors of each character get separated independently during gamete formation and again become re-arranged in off springs.
![]()
Question 20.
Write about three ecological pyramids with suitable examples.
Answer:
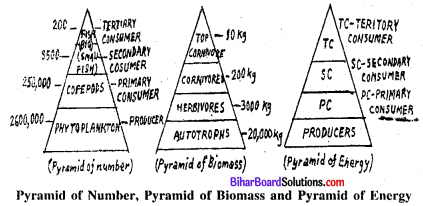
Ecological Pyramids. represents the humerical relationship between different trophic levels of a food chain. These are of three types:
(i) Pyramid of Number: It indicates that the producers which form the base of the Pyramid are ingested large numbers by a comparatively small number of primary consumers. These eaten by a small number of primary cornivoes, which is also ingested by still amall number of tertiary consumers or secondary carnivores.
(ii) Pyramid of biomass: The biomass i.e. the living weigst of the organismas of the food chin present at any time in an ecosystem forms the pyramid of biomass. The pyramid of biomass indicates the decrease in biomass ar each troth ic level from base to apex.
(iii) Pyramid energy: It indicates the total energy at each trophic level of this food chain. It also exhibits that at each trophic level loss of energy and material takes place as the process of assimilation and growth are not 100% efficient.
Question 21.
What is Gene therapy ? Describe it by using the example of adenosine diaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Answer:
Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allows correction of a gene defect that has been diagnosed in a child/embryo. Here genes are inserted into a person’s cells and tissues to treat a disease. Correction of a genetic defect involves delivery of a normal gene into the individual or embryo to take over the function of and compensate for the non-functional gene.
The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to a 4-year old girl with adenosine diaminase (ADA) deficiency. This enzyme is crucial for the immunical system to function. This disorder is caused due to the deletion of the gene for adnesinal diaminase. In some children ADA deficiency can be cured by bone marrow transplantation; in others it can be treated by enzyme replacement therapy, in which functional ADA is given to the patient by injection. But the
problem with both of these approaches that they are not completely curative. As a first step towards gene therapy, lymphocyte from the blood of the patient are grown in a culture outside the body. A functions ADA cDNA (using a retroviral vector) is then introduced into these lymphocytes which are subsequently returned to the patient. However, as these cells are no immortal the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes. However, if the gene isolate from marrow cells producing ADA introduced into cells at early embryonic stages, it could be a permanent cure.
Question 22.
What is Darwinism/Theory of Natural Selection?
Answer:
Darwinism is the theory of Natural Selection given by Charles Darwin. He supported evolution by following principles:
- Over production: Every organisms possess enormous fertility. They multiply in geometric ratio. But all of them do not survive.
- Limited food and space: Despite of rapid multiplication of all types of species, food and space resources remain limited, they are not liable to increase.
- Struggle for existence: Organism will have struggle for their existence. It may be intraspecific, Interspecific and environmental.
- Survival of the fittest: The organisms which are provided with favourable variations would survive because they are the fittest to face their surrounding, whole the unfits are destroyed.
- Inheritance of useful variation: Such useful variations are transmitted to the next generation while non useful variations are eliminated.
- Formation of new species : Such useful variations appear more prominantly in succeeding generations. And finally formation of new species takes place.
![]()
Question 23.
What do you understand by crossing over ? Decribe the mechanism of crossing over with suitable diagram.
Answer:
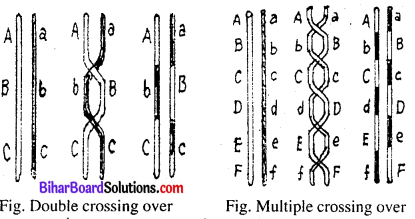
Crossing over is a recombination of genes due to exchange of genetic material between two homologous chromosomes. It is the mutual exchange of sigments of genetic material between nonsister chromatids of two homologers chromosomes. So as to produce recombinations or new combinations of genes.
The nonsister chromatids in which exchange of segments has occured are called recombinants or cross overs while the other chromatids in which crossing over has not taken place are known as parental chromatids or non-cross-overs.
Mechanism of crossing over: Chromosomes get replicated in S-phase of interphase. Therefore, leptotene chromosomes are double stranded though the two strands are not visible due to presence of nucleoprotein complex in between the chromatids.
- First of all homologous chromosomes pair.
- Each member of pair devide into two chromatids. Thus each monovalent chromosome becomes bivalent.
- If crossing over takes place then one chromosome twist-around the corresponding chromatid of the other chromosome.
- At this point break occurs and broken par of one chromatid join the other broken part of other corresponding chromatid resulting in exchange of chromatid parts containing the genes.
- The point at which crossing over takes place is called chiasmata.
Now each centromere of the homologous chromosome starts to separate from each other and the point of crossing over shifts towards the head of the chromosome. This movement of chiasmata is called criminalization. At the end of this the chromatids get separated.
Question 24.
Give an account of Pond Ecosystem.
Answer:
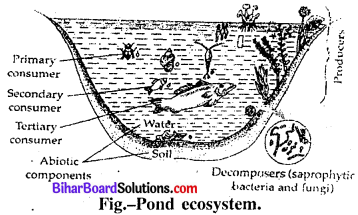
Pond Ecosystem: A small freshwater pond is a classic example of an ecosystem (aquatic). The follow¬ing two components are found in this ecosystem
(i) Abiotic components – The gases like CO2 – O2and other gases and inorganic substances are dissolved in pond water. Some abiotic components are found on the bottom of the pond. lit presence of sunlight, the green aquatic plants and algae manufacture the food material by photosynthesis with the help of CO2 and water which is essential for different organisms. After the death of these plants and animals, the complex matter decomposes and goes into water again as abiotic component and thus ecosystem continues forever.
(a) Producers – All the green plants found in the pond e.g. Hydrilla, Marsilia, Ranunculus etc. and different types of Algae, Spirogyra, Volvox, Nostoc are examples of producers. All these producers prepare food by photosynthesis.
(b) Consumers – These can be divided into the following categories:
(iv) Primary Consuniers – Various types of small insects and their larvae, herbivores and fishes are primary consumers.
(v) Secondary consumers-These consumers are primary carnivores which eat the herbivores, e.g. frog, water snakes, bettles & some fishes etc.
(vi) Tertiary consumers-Carnivores fishes are found in the pond water which feed on the consumers of second-order small fishes.
(c) Decomposers – Various types of microorganisms eg. bacteria, fungi etc. are also present in the pond water which are called decomposers. They attack on dead bodies of producers and consumers and convert complex organic compounds into simple inorganic compounds.
![]()