BSEB Bihar Board 12th Accountancy Important Questions Long Answer Type Part 5 are the best resource for students which helps in revision.
Bihar Board 12th Accountancy Important Questions Long Answer Type Part 5 in English
Question 1.
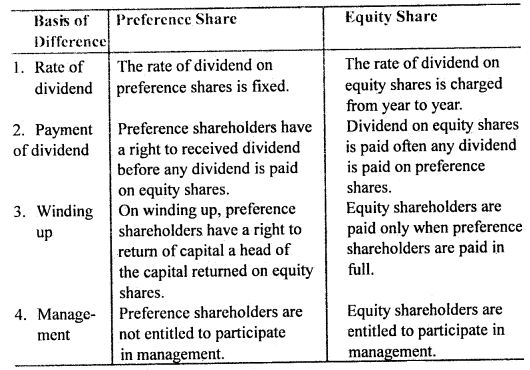
Difference between preference share and equity share.
Answer:
The difference between preference share and equity share are as follows:
Question 2.
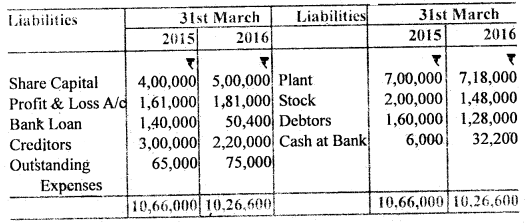
From the following Balance Sheets as of 31st March 2015 and 2016, you are required to calculate Cash Flow from Operating Activities for the year ended 31st March 2016:
Balance Sheets
(as of 31st March 2015 and 2016)
Answer:
Calculation of Cash Flow from Operating Activities
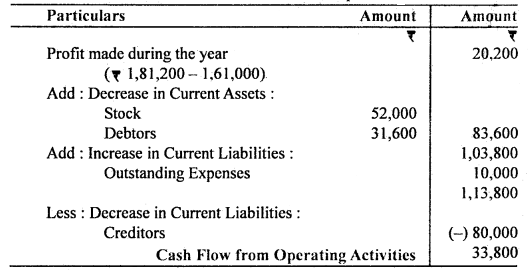
Note: Bank Loan has been assumed as a non-current liability.
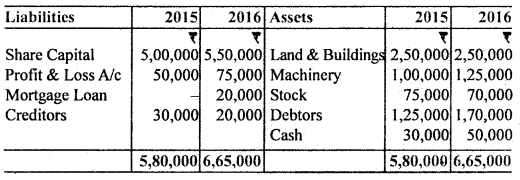
Question 3.
From the following Balance Sheet of M. Ltd., prepare Cash
Answer:
Cash Flow Statement (Indirect Method)
(for the year ended 31 st March 2016)


Question 4.
Prepare Cash Flow Statement from the Balance Sheet of Mohan Ltd. for the year ended 31st March 2016:
Balance Sheet
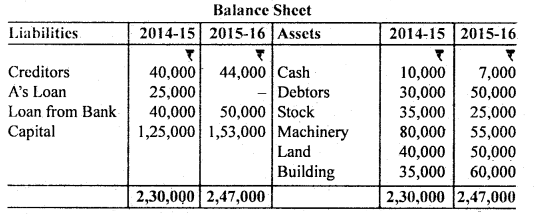
During the year, a machine costing 10,000 (accumulated depreciation ₹ 3,000) was sold for ₹ 5,000. Depreciation provided during the year was ₹ 18,000. Prepare Cash Flow Statement.
Answer:
Cash Flow Statement
(for the year ended 31 st March 2016)


Question 5.
Discuss the features of u company.
Answer:
Essential features of a company: Following are the essential features (characteristics) of a company.
- Association of persons: A company is an association of persons, usually for profit.
- Artificial person: It is an artificial person created by law.
- Separate legal entity: It has a separate legal entity from its members. So, it can sue and can be sued in its own name. It can own or dispose of the property in its own name.
- Limited liability: It has limited liability. The liability of members is limited to the extent of the face value of shares held by them.
- Perpetual succession: A company is an artificial person who never dies. It has continuous existence. It is a creation of law. So, its existence can be terminated only by law. It is not affected by the death of its members.
- Common seal: It has a common seal that acts as the official signature of the company. Any document without the common seal of the company is not binding up the company.
- Transferability of shares: The capital of a company is divided into shares. The shares of a company are freely transferable except in the case of a private company.
- Separation of ownership and management: In companies, there is a divorce between ownership and management. It is owned by members (i.e., shareholders but it is managed by the Board of Directors who are elected by shareholders. Members of a company can not directly participate in the management of the business of the company.
Question 6.
A and B are in partnership sharing profits and losses in the proportion of 3/5 and 2/5. The following was their Balance Sheet as of 31st March,12016:
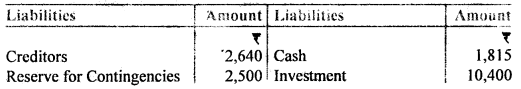
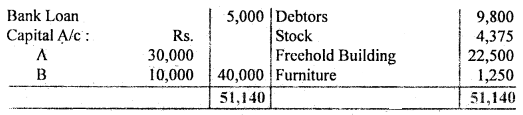
They decided to dissolve the partnership on this date and the assets, with the exception of the investment and cash, were sold for Rs. 34,000. The market value of Investment was Rs. 11,000 which was taken over by B who also agreed to discharge Bank Loan. The expenses of winding up were Rs. 550. The creditors were paid Rs. 2,515 in full settlement.
You are required to prepare Realisation A/c, Cash A/c, and Partners Capital A/c.
Answer:
Realisation Account
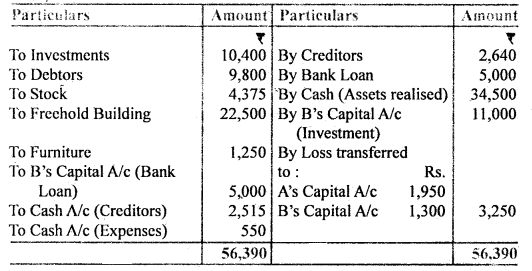
A’s Capital Account
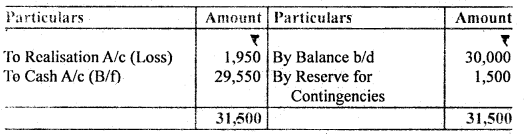
B’s Capital Account
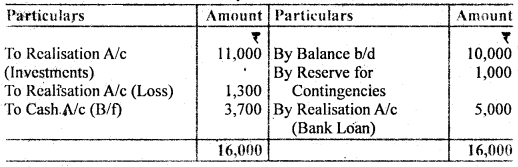
Cash Account

Question 7.
Calculate Cash flow from operating activities from the following Profit & Loss A/c:
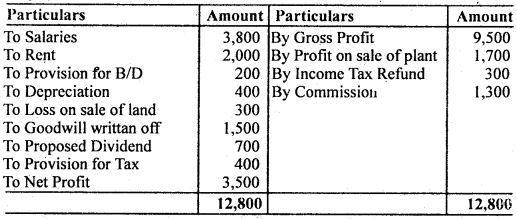
Answer:
Cash Flow from Operating Activities

Working Notes:
Calculation of Profit before Tax

Question 8.
What is a partnership? What are its chief characteristics? Explain.
Answer:
Meaning of Partnership:
The partnership is an agreement written / oral between two or more persons who have agreed to do some lawful business and to share profit or loss arising from the business.
According to the Indian Partnership Act, 1932, Section – 4, “Partnership is the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all or any of them acting for all.”
In partnership, two or more persons join hands to set up a business and share its profits and losses.
Persons who have entered into a partnership with one another are called individually partners and collectively ‘a firm’ and the name under which their business is carried on is called the ‘firm name’. A partnership firm is not a separate legal entity apart from the partners constituting it.
There must be a minimum of two persons to form a partnership firm, according to the Indian Partnership Act, 1932, but it does not specify the maximum number of partners. In this issue section, 11 of the companies act 1956 limits the number of partners to 10 for a partnership carrying on banking business and 20 for a partnership carrying on any other type of business.
Characteristics of Partnership:
1. Two or more persons: There meant to be a minimum of two persons to form a partnership firm, according to the Indian Partnership Act, 1932, but it does not specify the maximum number of partners. In this issue Section 11 of the Indian Companies Act, 1956. limits the number of partners of 10 (ten) for a partnership carrying on banking business and 20 (twenty) for a partnership carrying on any other type of business.
2. Agreement: Partnership comes into existence on account of an agreement among the partners, and not from the status or operations of the law. The agreement becomes the basis of the relationship between the partners. It may be written or oral. It may be for a fixed period or for a particular venture or at will.
3. Business: A partnership can be formed for the purpose of carrying on some lawful business with the intention of earning profits. Mere co-ownership of a property does not amount to a partnership.
4. Mutual agency: The partnership business may be carried on by all the partners or any of them acting for all. This statement means that every ‘ partner is entitled to participate in the conduct of the affairs of its business and there exists a relationship of mutual agency between all the partners. Partners are agents as well as principals for all other partners. Each partner can bind other partners by his acts and also is bound by the acts of other partners with regard to the business of the firm. The relationship of the mutual agency is so important feature of partnership that one can say that there would be no partnership if this feature is absent.
5. Sharing of profit: The agreement between the partners must be to share the profits (or losses). Though the definition of partnership, according to Partnership Act, describes partnerships relation between people who agree to share the profits of a business, the sharing of loss is implied. If some persons join hands for the purpose of some charitable activity, it will not be termed as a partnership.
6. Liability of partnership: The liability of partnership is unlimited. Each partner is liable jointly with all the other partners and also individually to the third party for all acts of the firm done while he is a partner.
Question 9.
Why there is a need for the revaluation of assets and liabilities on the admission of a partner?
Answer:
At the time of admission of a partner, it is necessary to assess the correct and current value of assets and liabilities of the firm shown in books because the current value of various assets and liabilities may be different from the values shown in the balance sheet. To revalue the assets and liabilities new account is opened called Revaluation Account. To revenue the assets and liabilities, all necessary adjustments are made through the Revaluation Account or Profit and Loss Adjustment Account.
Revaluation of assets and liabilities is needed at the time of admission so that the profit or loss arising on account of such revaluation maybe adjusting the old partner’s Capital Account in Old profit sharing ratio and the new partner may not be affected by the profit or loss on account of revaluation of assets and liabilities.