Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Model Papers
Bihar Board 12th Chemistry Model Question Paper 1 in English Medium
Time : 3 Hours 15 Min
Full Marks: 70
Instructions for the candidates
- Candidates are required to give answers in their own words as far as practicable.
- Figures in the right hand margin indicates full marks.
- While answering the questions, candidate should adhere to the words limit as far as practicable.
- 15 Minutes of extra time has been allotted for the candidates to read the questions carefully.
- This question paper is divided into two sections : Section -A and Section-B
- In Section A, there are 35 objective type questions which are compulsory, each carrying 1 mark. Darken the circle with blue/black ball pen against the correct option on OMR Sheet provided to you. Do not use Whitener/Liquid/Blade/ Nail on OMR Sheet otherwise your result will be treated as invalid.
- In section-B, there are 18 short answer type questions (each carrying 2 marks), out of which only 10 (ten) questions are to be answered Apart from this there are 06 Long Answer type questions (each carrying 5 marks), out of which 3 questions are to be answered.
- Use of any electronic device is prohibited.
Objective Type Questions
In the following questions no. from 1 to 35, there is only one correct answer against each question. For each question, mark (darken) the correct answer on the OMR Sheet provided to you. (1 x 35 = 35)
Question 1.
How many types of Crystals are found ?
(a) 2
(b) 6
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer:
(c) 4
Question 2.
Which of the following bond is found in H2O (ice)?
(a) Hydorgen bond
(b) Metallic bond
(c) Ionic bond
(d) All
Answer:
(a) Hydorgen bond
![]()
Question 3.
One Faraday of electricity is equal to how many coulombs ?
(a) 96500
(b) 96550
(c) 94500
(d) 96000
Answer:
(a) 96500
Question 4.
Inverse of resistance is called ………..
(a) Conductance
(b) Resistance
(c) Good conductor
(d) None
Answer:
(d) None
Question 5.
For strong electrolytes λm ………..
(a) increases on dilution
(b) decreases on dilution
(c) remains constant on dilution
(d) All
Answer:
(a) increases on dilution
![]()
Question 6.
Chemisorption is ………..
(a) Irreversible in nature
(b) Reversible in nature
(c) Arises due to Van-der-Waals forces
(d) Depends on nature of the gas
Answer:
(a) Irreversible in nature
Question 7.
Chief ore of Iron is ……..
(a) Magnetite (Fe3O4)
(b) Haematite (Fe2O3)
(c) Siderite (FeCO3)
(d) Iron pyrite (FeS4)
Answer:
(b) Haematite (Fe2O3)
Question 8.
Which type of ore can be concentrated by Electromagnetic separation method
(a) Non-magnetic particles
(b) Magnetic particles
(c) Sulphide ores
(d) All the above options
Answer:
(b) Magnetic particles
![]()
Question 9.
Copper matte contains :
(a) Cu2S and Cu2O
(b) Cu2S and FeS
(c) CuS2 and Fe2O3
(d) Cu2S and Cu
Answer:
(b) Cu2S and FeS
Question 10.
Group 15 of Periodic Table includes Nitrogen and …………..
(a) Oxygen
(b) Phosphorous
(c) Carbon
(d) Argon
Answer:
(b) Phosphorous
Question 11.
d-block elements are also known as …………….
(a) Transition elements
(b) Typical elements
(c) Non-transition elements
(d) Alkali metals
Answer:
(a) Transition elements
Question 12.
d-block elements are also known as ………….
(a) Transition elements
(b) Typical elements
(c) Non-transition elements
(d) Alkali metals
Answer:
(a) Transition elements
![]()
Question 13.
Zinc is a ………..
(a) Transition element
(b) Lanthanide
(c) Normal element
(d) Element of s-block
Answer:
(c) Normal element
Question 14.
Mn3+ is an oxidising agent because………..
(a) half filled K2-level
(b) Completely filled eg level
(c) empty d-orbital
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) half filled K2-level
Question 15.
U.P.A.C name of K2[Zn(OH)4] is………..
(a) Potassium tetrahydroxoxincate (II)
(b) Zinc di-hydroxide
(c) Zinc hydroxide potassium
(d) None
Answer:
(d) Racemic mixture
Question 16.
The stereo isomens related to each other as non- super imposable mirror images are called
(a) diastereomers
(b) enantiomers
(c) chiral compound
(d) Racemic mixture
Answer:
(a) diastereomers
![]()
Question 17.
Chloroform on treatement with O2 in presence of light gives ………..
(a) Phosphene
(b) Phosgene
(c) Phosphorescence
(d) Methane
Answer:
(b) Phosgene
Question 18.
Alcohols and Phenols are formed when one of the hydrogen atom of Alkane and Arenes are replaced by which group ?
(a) – Cl
(b) – OH
(c) – CHO
(d) – COOH
Answer:
(b) – OH
Question 19.
Glycerol is a …………..
(a) Monohydric alcohol
(b) Di-hydric alcohol
(c) Trihydric alcohol
(d) Tetrahydric alcohol
Answer:
(c) Trihydric alcohol
Question 20.
Simplest hydroxy derivative of Benzene is ………….
(a) Propanol
(b) Phenol
(c) Benzylal cohol
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Phenol
Question 21.
IUPAC name of the compound

(a) 2, 5-dimethyl Phenol
(b) l-Hydroxy-2-methyl toluene
(c) 1-Hydroxy-2, 3-dimethyl benzene
(d) Hydroxy dimethyl benzene
Answer:
(a) 2, 5-dimethyl Phenol
Question 22.
Chloro-ethane on reacting with ammonia gives …………
(a) Ethanamine
(b) Propanamine
(c) Benzylamine
(d) Ethane nitrile
Answer:
(a) Ethanamine
Question 23.
Amides on reduction with LiAlH4 ………………
(a) Alkanes
(b) Alkylamines
(c) Alcohols
(d) Acids
Answer:
(b) Alkylamines
![]()
Question 24.
IUPAC name of HCOOH is …………..
(a) Ethanoic acid
(b) Formic acid
(c) Methanoic acid
(d) Oxalic acid
Answer:
(c) Methanoic acid
Question 25.
IUPAC name of Oxalic acid is …………..
(a) Metanoic acid
(b) Ethanoic acid
(c) Ethanedioic acid
(d) Benzene
Answer:
(c) Ethanedioic acid
Question 26.
The formula of Methylnitrile is ……………
(a) CH3NC
(b) CH3CN
(c) C2H5CN
(d) C2H5NC
Answer:
(b) CH3CN
Question 27.
Simple Carboxylic acid are soluble in water due to formation of………………………….
(a) Co-Valent bond
(b) Hydrogen bond
(c) Ionic.hood
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Co-Valent bond
Question 28.
The formula of Fructose is ……………
(a) C6H12O6
(b) C12H22O11
(c) C6H12O5
(d) C6hH6O6
Answer:
(b) C12H22O11
Question 29.
Carbohydrate that yields three to ten monosaccharides units on hydrolysis are called ………..
(a) Mono-saccharide
(b) Oligo-saccharide
(c) Poly-saccharide
(d) Di-saccharide
Answer:
(a) Mono-saccharide
![]()
Question 30.
Amino acid contains two functional groups, one is – COOH and other is …………
(a) – OH
(b) – NH3
(c) – NH2
(d) NH4
Answer:
(b) – NH3
Question 31.
Polymers of a-amino acid is called …………….
(a) Protein
(b) Peptines
(c) Peptides
(d) Dipeptides
Answer:
(b) Peptines
Question 32.
Polythene is a polymer of ?
(a) Ethane
(b) Ethene
(c) Ethyne
(d) Propene
Answer:
(b) Ethene
Question 33.
Rubber, Starch, Cellulose and Protein are ……………
(a) Synthetic polymers
(b) Natural Polymers
(c) Semi-Synthetic polymers
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Natural Polymers
Question 34.
Buna- N and Buna- S are the types of ……………….
(a) Natural rubber
(b) Synthetic rubber
(c) Polythene
(d) Bakelite
Answer:
(b) Synthetic rubber
![]()
Question 35.
The drug used to reduce fever is known as ………………..
(a) Antacid
(b) Analgesic
(c) Anti-pyretic
(d) Anti-biotic
Answer:
(c) Anti-pyretic
Non-Objective Type Questions
Short Answer Type Questions
In this Section, there are 18 Short answer type questions (each carrying 2 marks), out of which answer any 10 questions.
Question 1.
What do you mean by Frenkel’s Defect ?
Answer:
This defect is shown by those ionic solids in which there is a large difference in the size of ions,
e.g. ZnS, AgCl, AgBr, Agl.
Question 2.
What do you mean by an Ideal solution ?
Answer:
Ideal solutions obc, Rault’s law over entire range of concentration. For these solution Amix H = O and Amix V = O.
In binary solutions, if A – B interactions are nearly equal to A – A or B – B interactions then it is an ideal solution. Solutions of n -hexane & n-heptane, bromoethane & chloroethane, benzene & toluene, etc., are nearly ideal in behaviour.
Question 3.
Define Osmotic pressure ?
Answer:
The hydrostatic pressure which develops on account of osmosis is called Osmotic pressure or the excess pressure that must be applied on the solution to prevent osmosis is called Osmotic pressure.
Osmotic pressure (π) is directly proportional to molarity (C) of the solution at a given temperature π α C
\(\pi=\mathrm{CRT} \text { or, } \pi=\frac{n_{2}}{\mathrm{V}} \mathrm{RT}\left[\text { where }, \mathrm{C}=\frac{n_{2}}{\mathrm{V}}\right]\)
Question 4.
Why Copper sulphate is not stored in zinc pot ?
Answer:
Zinc is stronger reducing agent than copper. Thus zinc forms zinc sulphate during chemical reaction. Therefore, copper sulphate is not stored in zinc pot.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
![]()
Question 5.
In Nernst equation
\(\mathbf{E}=\mathbf{E}^{0}-\frac{\mathbf{R} \mathbf{T}}{\mathbf{n} \mathbf{F}} \mathbf{I n} \frac{[\mathbf{M}]}{\left[\mathbf{M}^{\mathbf{n}+}\right]} \mathbf{R}\)
Answer:
It gives the relation between electrode potential, temperature and concentration of metal Ions.

When T = 298 K, F = 96500 C mol-1
R = 8.314 J K-1 & concentration of solid M is taken as unity.
Question 6.
Define Cell Constant ?
Answer:
Cell constant : The quantity l/a is called cell constant where ‘l’ is the distance of two electrodes and ‘a’ is the area of cross section of electrode. It is expressed in the units cm-1.
\(Cell constant =\frac{\text { Distance between the electodes }}{\text { Area of Cross }-\text { Section }}\)
Question 7.
What are Enzymes ?
Answer:
Enzymes are complex nitrogenous organic compounds. They are usually protein molecules of high molecular mass. These are biochemical catalysts as numerous reactions that occur in the bodies of animals & plants to maintain the life process are catalysed by enzymes.
Question 8.
Why does PH3 fumes in moist air ?
Answer:
PH3 reacts with moist air to form impure phosphine, which bums in air and forms dense white smoke of metaphosphoric acid.
Question 9.
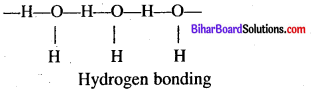
Why H2O is liquid and H2S is gas at room temperature ?
Answer:
H2O contains hydrogen bonding but H2S does not contain hydrogen bonding due to oxygen is more electronegative than sulphur.
Question 10.
On what ground you will say that, Scandium (Z = 21) is a transition metal ?
Answer:
The last electron of Scandium enters in 7-orbital. It has vacant 7-orbital.
Sc (Z = 21)-Is2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1, due to vacant 7-orbital & entering of last electron scandium is a transition element.
![]()
Question 11.
Which Ore is stronger reducing agent Cr2+ or Fe2+ ? Explain.
Answer:
Cr2+ is a stronger reducing agent than Fe2+.
This is quite evident form the E° values. E° Cr3+/Cr2+ = – 0.4/V and E° Fe3+/Fe2+ = 0.77 V.
Reason : T4 → 73 occurs when Cr2+ changes to Cr3+ ion while T6-) T5 takes place when Fe2+ gets converted to Fe3+ ion. Now d4 → 73 transition is easier as compared to T6 → T3 transition. Therefore, Cr2+ is a stronger reducing agent than Fe2+.
Question 12.
What do you mean by inner-transition elements ?
Answer:
The last electron added to each element is an f- electron. These two series of elements are hence called the inner transition elements (f-block Elements). The two rows of elements at the bottom of the Periodic Table, called the Lanthanoids, Ce (Z = 58) – Lu (Z = 71) & Actinoids, Th (Z = 90) – Lr (Z = 103).
Question 13.
What do you mean by co-ordination number ?
Answer:
Co-ordination number : The number of coordinate covalent & covalent bonds formed by the central metal of a complex compound is called co-ordination number of the central metal.
Example : [Ag (NH3)2]C1 C.N of Ag+ ion is 2.
Question 14.
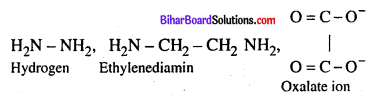
Define Bidentate Ligand ?
Answer:
Bidentate or didentate Ligands: Ligands which has two donar atoms and has tendency to attach to the central ion through two donar atoms. Examples are
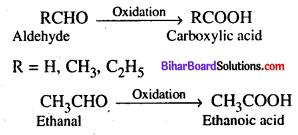
Question 15.
What Aldehyde on oxidation will give ?
Answer:
On oxidation aldehyde gives carboxylic acid
Question 16.
Name one water soluble and one fat soluble Vitamin.
Answer:
(a) Water soluble vitamins – (Vitamin B & C)
(b) Fat-soluble vitamins-(Vitamin A, D, E & K)
Question 17.
Define Molarity and Mole fraction.
Answer:
Molarity (M) : It is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved in one litre (or one cubic decimetre) of the solution.
\(\text { Molarity }(\mathrm{M})=\frac{\text { Number of moles of solute } \times 1000}{\text { Volume of solution }(\mathrm{m} l)}\)
Molality (m) : It is defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of the solvent.
\(\text { Molality }(\mathrm{m})=\frac{\text { Number of mol. of solute } \times 1000}{\text { Mass of solvent }(\mathrm{g})}\)
![]()
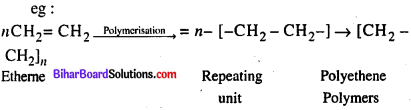
Question 18.
Differentiate between Condensation and Polymerisation.
Answer:
Condensation : The condensation polymers are formed by repeated condensation reaction between two monomeric units having different bifunctional and trifunctional groups with the elimination of small molecules like water, alcohol, hydrogen chloride etc.
Example : Nylon 6, 6

Polymerisation: The process of formation of polymers from respective monomers is called polymerisation,
Long Answer Type Questions
There are 06 long answer type questions (each carrying 05 marks), out of which answer any there questions.
(5 x 3 = 15)
Question 19.
Find the order of reaction of the following :
(a) Rate = K[A]1/2 [B]3/2
(b) Rate = K[A]3/2 [B]-1
Answer:
(a) Rate = K[A]1/2 [B]3/2
Therefore order = \(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{3}{2}=\frac{4}{2}=2\)
This is called second order reaction.
(b) Rate = K [A]3/2 [B]-1
Therefore, order = \(\frac{3}{2}+(-1)=\frac{3}{2}-1=\frac{3-2}{2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
This is first order of reaction
![]()
Question 20.
Write in brief about how Sulphuric acid is manufactured by Contact process ?
Answer.
Sulphuric Acid (H2SO4) : It is called the king of chemicals and is one of the most widely used industrial chemicals. Manufacture : Sulphuric acid is manufactured by contact process which involves 3 steps
- Burning of sulphur or sulphide ores in air to produce SO2
- Conversion of SO2 into SO3 by reaction with air in the presence of catalyst U2Os.
- Absorption of SO3 in H2SO4 to give Oleum (H2 S2 O7)
The key step is the catalytical oxidation of SO2 with O2 to give SO3 in the presence of V2O5.
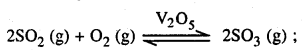
The SO3 gas is absorbed in concentrate H2SO4 to produce Oleum (H2S2O7) which on dilution with water gives H2SO4 of desired concentration.
SO3 + H2SO4 → H2 S2 O7 (Oleum)
H2S2O7+ H2O → 2H2SO4 The sulphuric acid obtained by the contact process is 96 – 98% pure.
Question 21.
What happens when.
(i) Concentrated H2S04 is added ict Calcium fluoride and heated ?
(ii) SO3 is passed through water.
Answer.
(i) When concentrated H2SO4 is added to calcium fluoride and heated it gives calcium sulphate (CaSO4) and hydrogen fluoride (HF)
CaF2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2HF
(ii) When SO3 is passed through water it gives sulphuric acid.
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Question 22.
Write the electronic configuration of the following :
(a) Cr3+ (b) Cu+ (c) CO2+ (d) Fe2+ (e)Mn2+ [Atomic number of Cr = 24, Cu = 29, Co = 27, Fe = Mn = 25]
Answer.
(a) Cr3+ – [Ar] 3d3 4s°
(b) Cu+ – [Ar] 3d10 4s°
(c) Co2+ – [Ar] 3d7 4s°
(d) Fe2+ – [Ar] 3d6 4s°
(e) Mn2+ – [Ar] 3d5 4s°
![]()
Question 23.
How will you convert the following ?
(a) Methane to Ethane
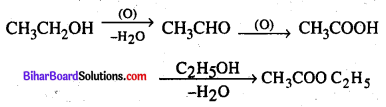
(b) Ethanol to Ethyl acetate
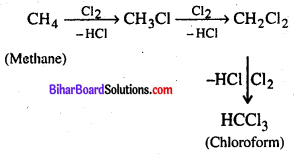
(c) Metane to Chloroform
(d) Ethanal to Ethanoic acid
(e) Acetic acid to methane
Answer.
(a) Methane to Ethane
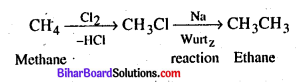
(b) Ethanol to Ethyl acetate
(c) Metane to Chloroform
(d) Ethanal to Ethanoic acid
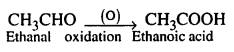
(e) Acetic acid to methane
![]()
Question 24.
Write short notes on
(a) Inductive effect
(b) Resonance
Answer.
Inductive effect: It is the process of displacement of electrons along, the chain of carbon atoms due to the presence of a polar covalent bond at one end of the chain. This is a permanent effect.
(a) – I effect: When the atoms or group of atoms of the polar covalent bond is more electro-negative than C, it is said to show -I effect.
![]()
(b) + I effect: If the substituent attached to the end of the carbon chain is electron donating, the effect is called + I effect.
![]()
Resonance : Molecules having two or more structures due to distribution of electrons but same molecular formula is called resonance.
e.g.Benzene molecule has the following structure.
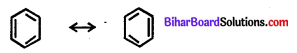
It is represented by a double headed arrow (<->) between the resonating structure.
Conditions :
- The nuclei in each of the canonical structures must be in the same relative position.
- The resonating structure differ only in the way of distribution of electrons.